Overview
The Delayer functions similarly to Minecraft's Repeater, but with more flexibility and precision. Like a Repeater, it can delay incoming signals and be locked by a second input. However, unlike a Repeater, the Delayer does not boost signal strength - it preserves the exact strength it receives.
The Delayer reads its primary input signal from Pin Mark A and stores it. On the next game tick, it reads the next signal and adds it to an internal queue. Each tick, the Delayer outputs the next stored value in that queue, creating a programmable delay line.
The delay queue can be set anywhere between 1 and 8 game ticks (note: these are Game Ticks, not Redstone Ticks). Applying any signal greater than 0 to Pin Mark B locks the queue, preventing it from updating until the lock is removed.
Because the Delayer can operate with a minimum delay of just one tick, it can be used to create clocks of up to 10 Hz. Traditional redstone timing normally peaks at 5 Hz unless complex structures are used.
The Delayer was designed to provide controllable latency in RedstoneCG circuits, which typically resolve their logic in a fraction of a tick - extremely fast, but computationally expensive. Introducing deliberate delay smooths update flow and helps reduce CPU load for intensive builds.

Configuration
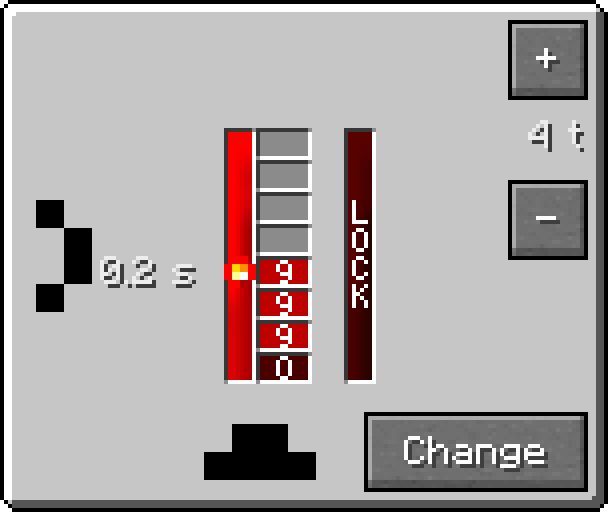
After placing a Delayer, you can open its configuration GUI by right-clicking it with an empty main hand (or with a hand holding non-Delayer items). This GUI is similar to the Analog Source interface.
- "Change" - cycles the input configuration (Pin Marks).
- "+" - increases delay by 1 tick.
- "-" - decreases delay by 1 tick.
The GUI displays the entire signal queue from bottom to top, ending at the Redstone Torch icon. It also visually indicates whether the Delayer is currently locked. The surrounding border shows the current pin configuration.
You can also configure Delayer without GUI:
- Crouch + Right-Click - change input configuration.
- Right-Click a Delayer with another Delayer - adjust the delay value.